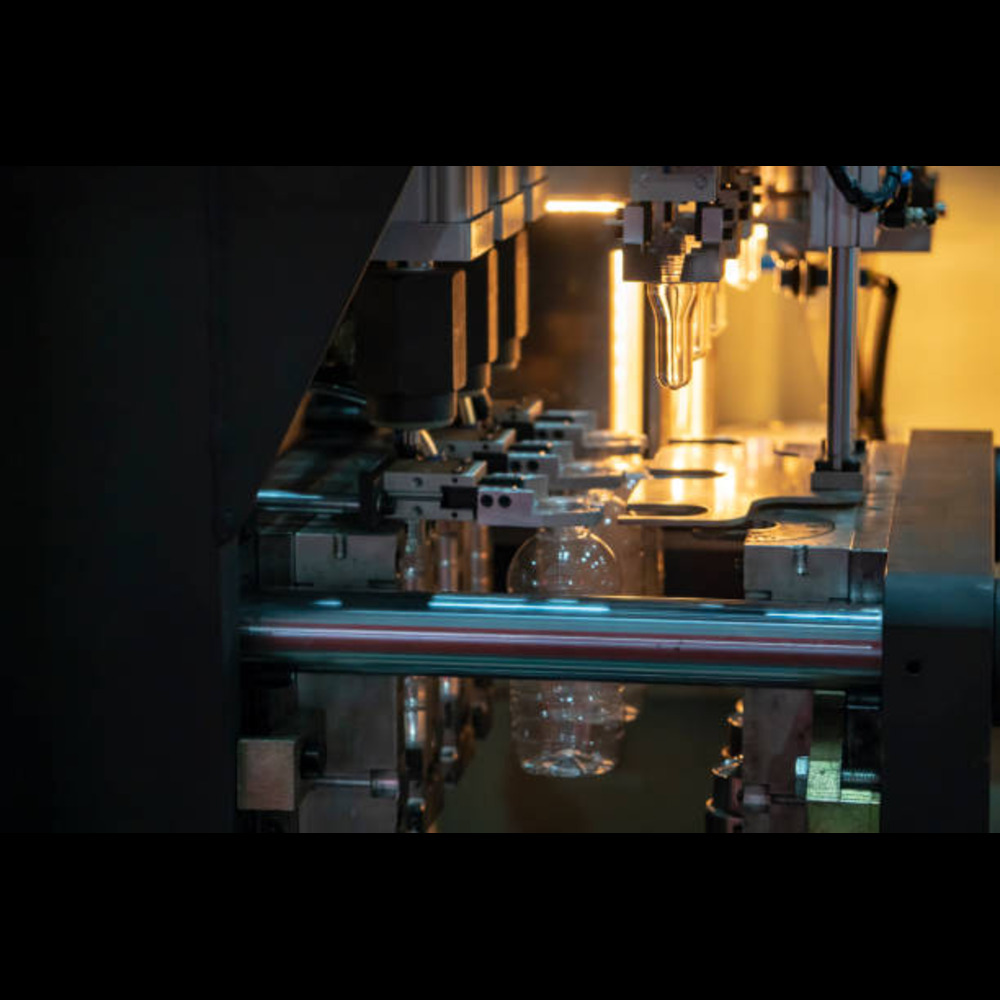
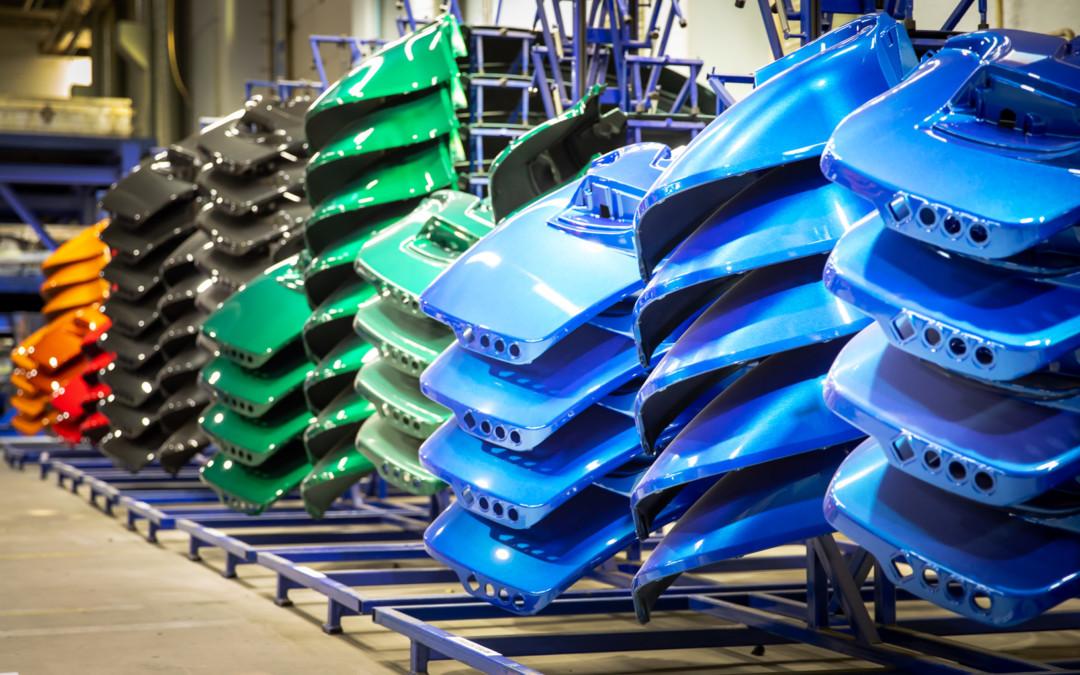
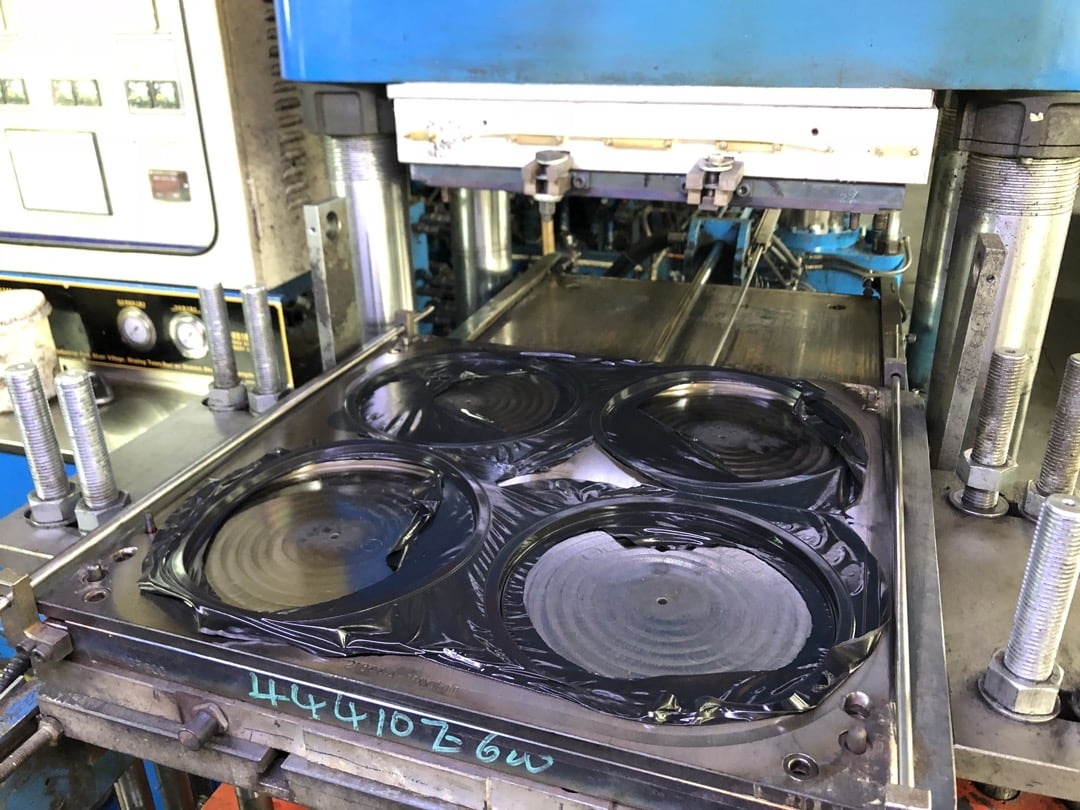
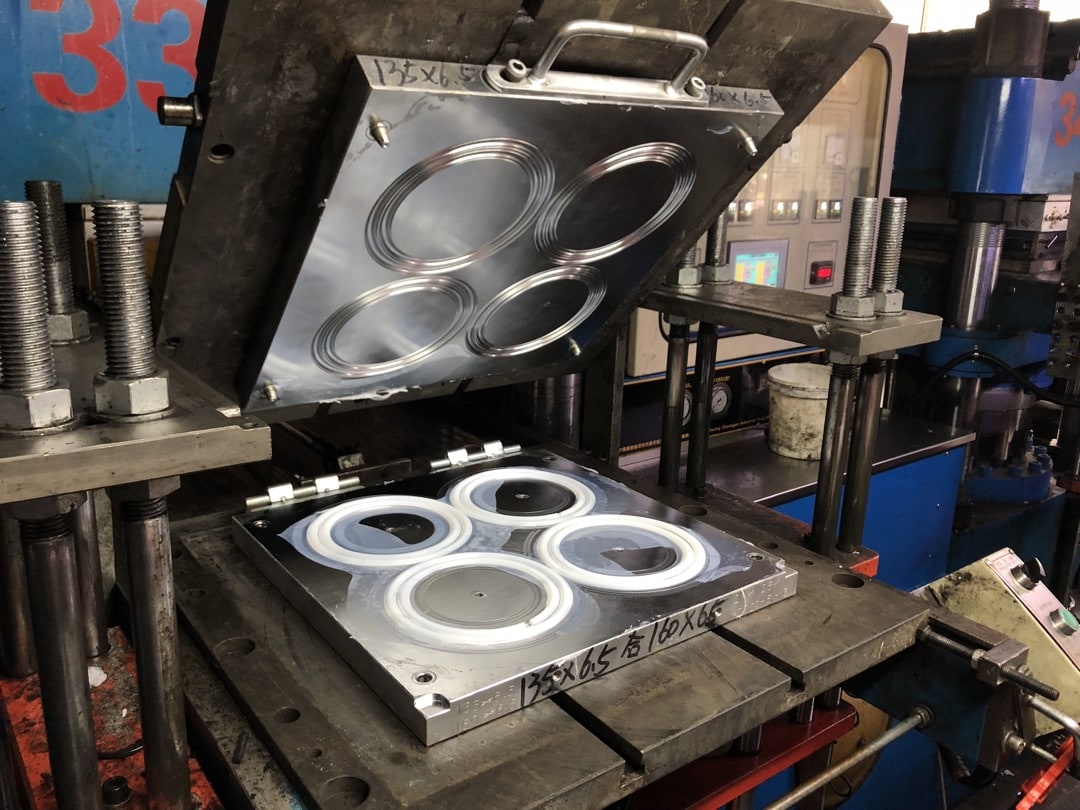
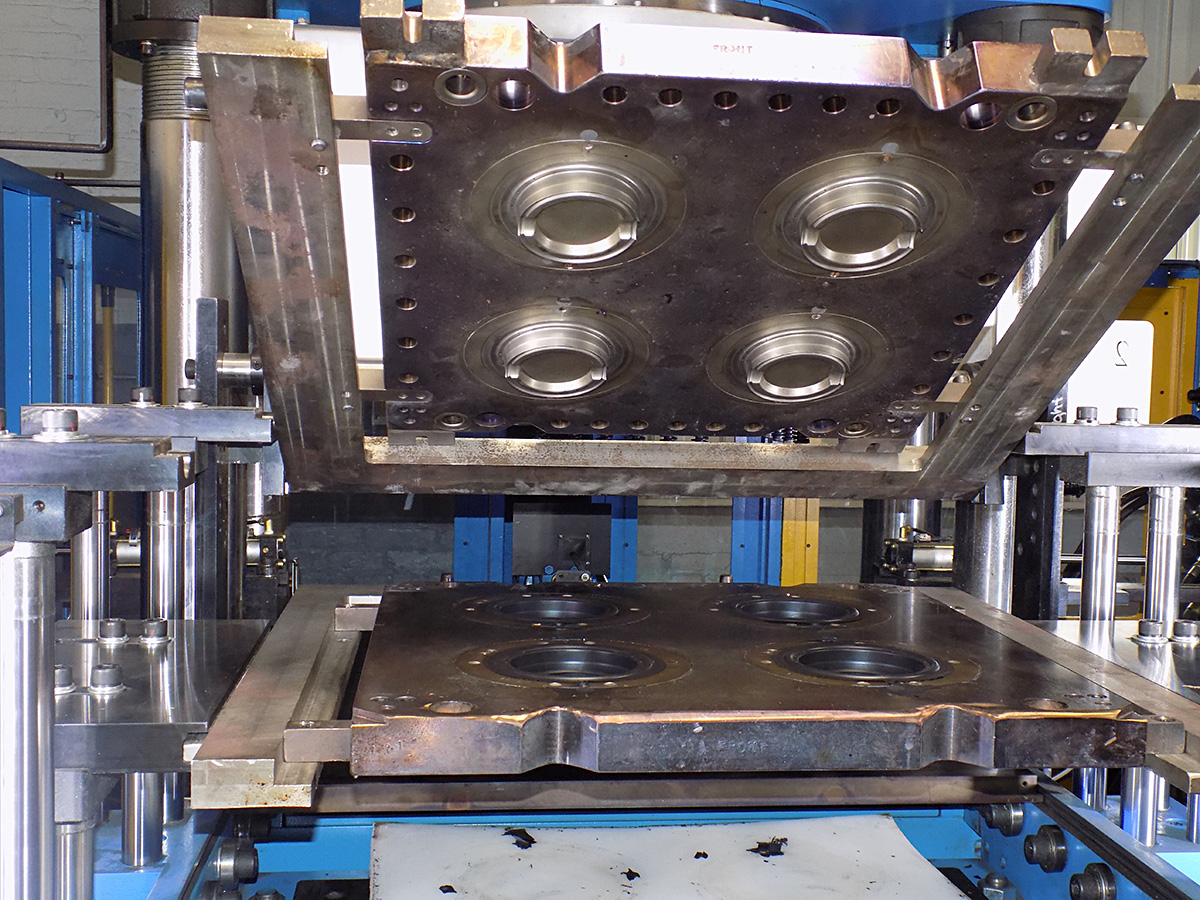
Manufacturing processes transform raw materials into finished products. One such process is Blow Molding. Generally, the blow molding process is used to create hollow plastic products. Our everyday items like bottles and containers are being manufactured using the blow molding process.
The knowledge about these processes enables you to make better decisions, have efficient communication with production teams, and helps you identify areas for improvement in the supply chain.
We TOPGRID provide you with a detailed explanation of Blow Molding. In this article, let’s see,
- What is Blow Molding?- Definition.
- Blow Molding Process
- Materials used in the Blow Molding process
- Advantages of Blow Molding
- Disadvantages of Blow Molding
- Applications of Blow Molding
What is Blow Molding ? – Definition
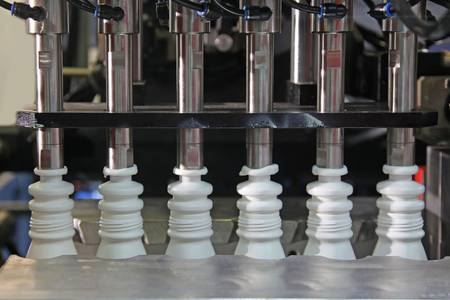
Blow molding is a versatile and cost-effective process that is used to produce a wide variety of products like bottles, containers, toys, and automotive parts.
The Basic principle of blow molding is to inflate a heated plastic tube (commonly known as preform or parison) inside a mold. That is, compressed air is blown into the plastic tube, which is kept inside the mold, causing it to expand and get the shape of the mold.
Generally, the blow molding process is as common as the injection molding process, employed by various industries for manufacturing their specific products.
To learn more about the difference between injection molding and blow molding you can check out our blog,
When it comes to blow molding the process is a relatively simple process compared to other manufacturing processes. Let’s dive into the detailed explanation of the step-by-step work process of blow molding!
Blow Molding Process

The blow molding process involves the following steps,
Step 1
The raw plastic material is fed into a hopper and conveyed to the extruder. The extruder heats and melts the plastic pellets. It then gets converted into a viscous molten plastic. This molten plastic is then forced through a die orifice to form a plastic tube called a parison.
Step 2
The prison is extruded into a cooling chamber. There it gets partially solidified to the desired wall thickness. And the length of the parison is controlled to match the dimensions of the final product.
Step:3
The mold consists of two halves. The parison is transferred to the mold. The mold halves close around the parison, trapping it within the cavity.
Step:4
A blowing nozzle is inserted into the parison. The compressed air is blown into the plastic tube (parison). The pressurized air forces the parison to expand and conform to the shape of the mold cavity, forming the hollow product.
Step:5
Once the parison has expanded and filled the mold cavity, the blowing air is stopped. The mold is allowed to cool. This cooling process solidifies the plastic, allowing the product to retain its shape.
Step:6
After the product has cooled sufficiently, the mold halves open. The finished product is ejected.
Step:7
Excess plastic material such as the flash or gate vestige, is trimmed from the product using a trimming machine.
Depending on the specific product requirements, additional post-processing steps (such as annealing, decorating or assembling multiple parts) may be performed.
Thus this is the overview of the blow molding process and there are three common types of blow molding.
They are,
- Extrusion Blow Molding
- Injection blow molding
- Injection Stretchblow molding
Learning about it provides you insights into cost structures, production efficiency, and quality control.
Material used in Blow Molding
When choosing materials, you must understand the specific requirements of products needed to produce. You have to choose according to it.
There are various types of materials used in blow molding, used to manufacture different products.
They are as follows:
Thermoplastics:
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
- Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
Engineering Plastics:
- Nylon (PA)
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
- Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)
Specialty Materials:
- Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG)
- Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
- Cyclic olefin copolymer (COC)
- Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA)
- Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE, TPR, TPO)
Note: Always consult with a materials engineer or a manufacturing specialist to determine the most suitable materials for your specific application.
Advantages of Blow Molding
Generally the blow molding process is an efficient and effective manufacturing process. It offers several advantages.
They are as follows:
- Blow molding is a relatively quick manufacturing process. The molds used are often less expensive compared to other manufacturing methods. Thus making it efficient and cost-effective for mass production of hollow plastic parts.
- Blow molding offers design flexibility. It allows for the production of complex shapes and intricate details in the final products.
- Blow molding enables the production of lightweight yet durable plastic products. This especially benefits manufacturing bottles where reducing weight can impact transportation costs and environmental considerations.
- The blow molding process allows for the creation of parts with consistent wall thickness. That ensures structural integrity and product quality.
- Blow molding is suitable for large-scale products. Its ability to produce a high volume of parts in a short time makes it suitable for various applications.
Thus these are the major advantages of the blow molding process. But before choosing any processes, you have to look at their limitations too. Let’s see the disadvantages of the blow molding process.
Disadvantages of Blow Molding
The blow molding process, though it offers you several advantages, also has some limitations or potential drawbacks that you should consider before choosing this method of manufacturing.
They are,
- The process is primarily suited for certain types of plastic. This limits the range of materials that can be used in blow molding.
- Molds are often less expensive, but the initial tooling costs for blow molding can be relatively high. This makes it less cost-effective for small production runs or prototypes.
- Setting up and adjusting the machinery for blow molding can take a considerable amount of time. This affects production efficiency.
- Blow molding is more suitable for producing larger, hollow items. This may not be practical for smaller and more intricate components.
- The blow molding process may generate waste material in the form of excess plastic, commonly known as flash. This needs to be trimmed off, contributing to material waste.
Thus these are limitations of using the blow molding process. You must carefully consider both benefits and limitations and assess their impact on the specific application before making a decision!
Applications of Blow Molding
Blow molding has found its application in various industries. You may find that many of our everyday objects are being manufactured using blow molding.
Here are some common industries and products where blow molding is effectively employed.
Bottles and Containers:
Blow molding is used for manufacturing plastic bottles and containers for,

- Beverages
- Household products
- Personal care items
Automotive Components:
Blow molding’s ability to create large, lightweight, and durable components is used to produce various automotive components. Such as,
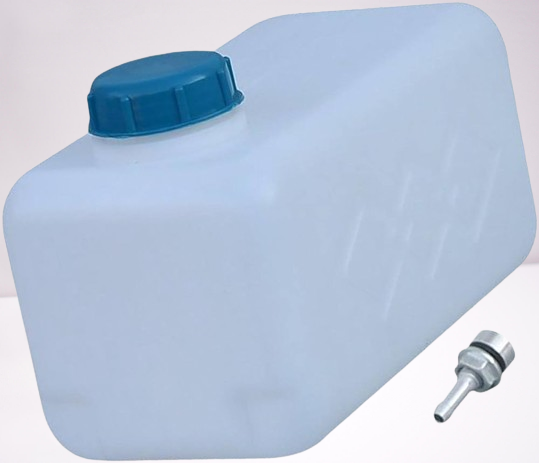

- Fuel tanks
- Air Ducts
- Reservoirs
Packaging Materials
The blow molding process is used for manufacturing packaging materials like,

- Plastic drums
- Jerry cans
and other packaging solutions for the transportation and storage of liquids.
Household items
Various household items including,

- Storage containers
- Buckets
- Cleaning supplies
are manufactured using blow molding.
Medical Devices
Blow molding is used to make a variety of medical devices, such as

- Catheters Balloons
- sample containers
- chambers
Blow molding does not stop here. It is also used to manufacture pipes and fittings, thus finding its applications in plumbing, irrigation, and drainage systems. As we mentioned before a lot of our everyday objects are being manufactured using blow molding. Thus making it a versatile manufacturing process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blow molding stands as a versatile and widely utilized manufacturing process, particularly in the production of hollow plastic products.
Its applications span various industries, from packaging and automotive to toys and medical equipment. Understanding the specific requirements of your project is crucial for determining whether blow molding is the most suitable method.
How TOPGRID can help you ?
We TOPGRID, your manufacturing partner, offer you 50+ such manufacturing processes.
You can choose as per your product needs. We’re dedicated to upholding the highest standards of quality throughout every stage of your manufacturing process. From the initial design to the final product completion, we assure you that the materials that undergo these processes and the products produced are quality-checked.
You can completely rely on Us! We simplify your complicated manufacturing processes!
GET YOUR QUOTE TODAY!
Topgrid – Blow Molding Service

- At Topgrid, we pride ourselves on being a best provider of Blow Molding Services.
- With a strong commitment to precision, innovation, and customer satisfaction, we are your trusted partner for all your plastic injection molding needs.